Privacy Preserving ML Application - PoC Design
Github Link
Homomorphic Encryption:
The key is to allow the computation on the encryption data. Thus the data can remain confidential while it is processed. In mathematics, homomorphic is the transformation of one dataset into another while preserving the relationship between elements in both sets.
Types of Homomorphic Encryption
-
Partially HE (PHE) : It allows only select mathematical functions to be performed on encrypted values. That means only one operation can be performed an unlimited number of times on the ciphertext.
-
Somewhat HE (SHE) SHE supports select operation (either + or *) up to a certain complexity, but there operations can only be performed a set number of times
-
Fully HE (FHE) FHE is capable of performing both addition and multiplication any number of times and makes secure MPC more efficient. It can handle arbitrary computations on the ciphertexts The goal of FHE is to allow the encrypted data to perform useful operations , such as ML without access to the encryption key. The security of the homomorphic encryption schemes are based on the Ring-Learning With Errors (RLWE) problem, which is a hard mathematical problem related to high-dimensional lattices. Most HE schemes are considered to be secure against quantum computers and making them in fact more secure than factorization and discrete logarithm based systems such as RSA and other forms of encryption.
HE Applications Scenarios:
- Securing Cloud Data Storing Secure data in the cloud while retaining the ability to calculate and search cipered information that you can decrypt local without compromising
- Enabling Data Analytics and ML in Privacy Preserving way It can be used for businesses and organizations across various industries including financial services, retail, information technology and healthcare to allow third parties to use data without seeing its unencrypted values.
- Preserving customers’ privacy in personalized marketing campaign and advertising
- Predictive analytics in healthcare
- Financial Services, Insurances..
- Call Tracking for Call Centers
- Government, Elections..
- Horizontal data silo integration
Limitations:
Multiple users: for an efficient way, separate data sources for every user. Computational Overhead Implementations: Microsoft SEAL: So far , the best one Google’s Private Join and Compute: focused on data analytics IBM’s HElib: too slow
Contextual Data in the edge:
There are three main source categories for contextual data: third-party businesses and organizations, customers, and things. Here are examples of the kinds of contextual data you could extract from each type:
- Businesses and organizations
- Weather
- News
- Events
- Traffic
- Economic/market changes
- Customers
- Social media activity, Calendar Events Data
- Past buying behavior
- Preferences
- Location
- Milestones
- IoT
- Delivery trackers
- Asset and inventory management sensors
- Kiosk interactions
- GPS tools
- Context-aware promotion tools
- Insight Data
- Images
- Audio
- Texts
PoC Data Model
- Location
- Location address with Place of Interests
- Images - inference the recent images
- Dectection: Person, Objects, Animals and others
- App activities
- Apps types and screen time
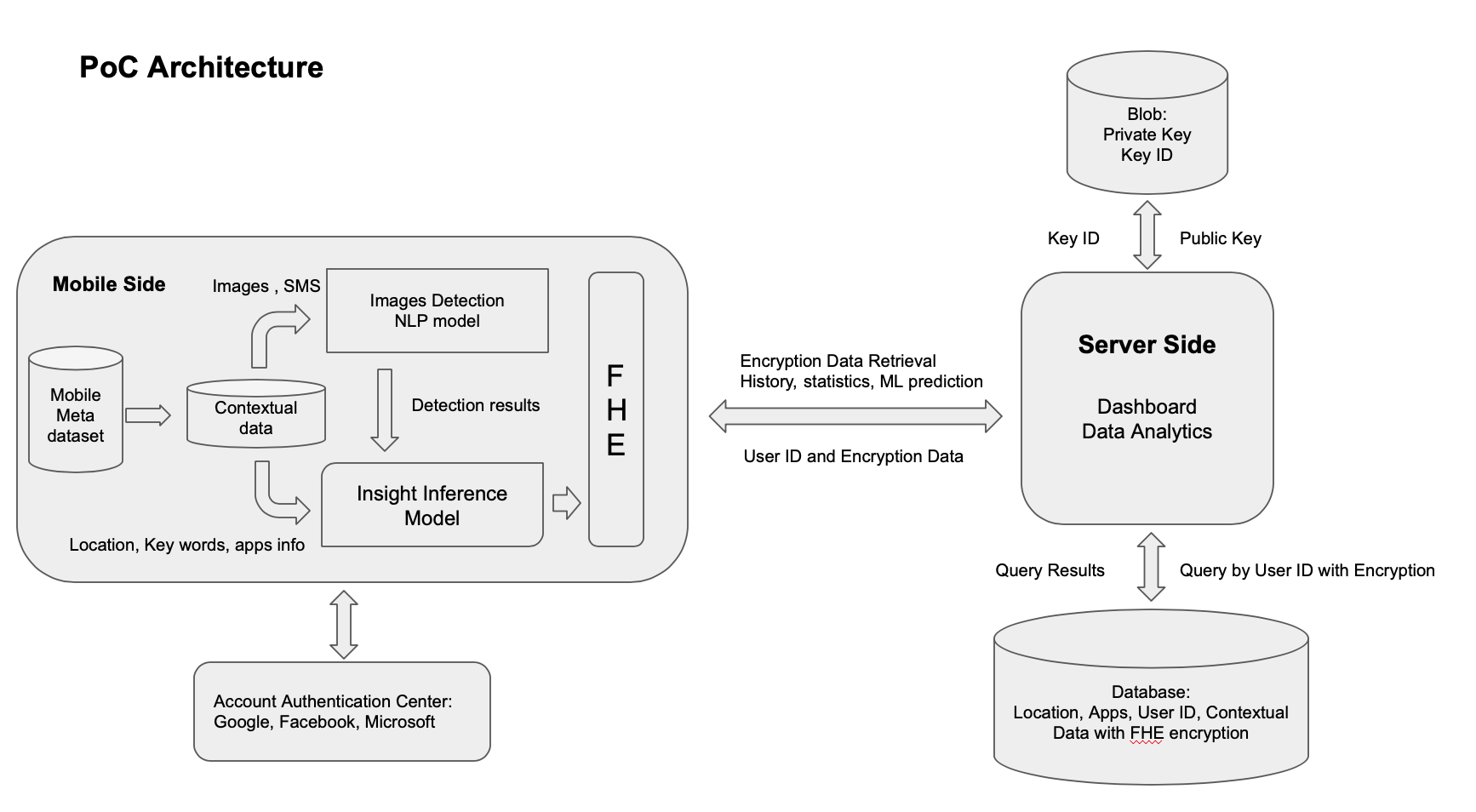
Archtecture
- Mobile Side:
- detection model for images detection/classification
- machine learning model for inference: data: images detection results, time, location(POI types - supermarkets, gym, pet store, coffee shops), app types(social media, gaming etc.) , google search key words
- Server side:
- Dashborad for encryption data
- Data Analytic Pipeline
- End-to-end Privacy Preservering Pipeline
- Mobile side: Federated Learning model, data with private key
- Data Transfer: Fully Homomorphic Encryption
- Server side: Encryption Data with public key
Application Cases
- Sports Fan Engagement Application
- Real Estate Lead Management