RSNA Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection
Project Overview
Deep Learning techniques have recently been widely used for medical image analysis, which has shown encouraging results especially for large healthcare and medical image datasets. In the computer vision field, the deep learning model, such as Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) has shown better capabilities to segment and/or classify medical images like ultrasound and CT scan images in comparison to traditional machine learning techniques. Recently, Deep Learning applications, in particular in applying the CNN model for analyzing Medical Images have achieved very promising results. The major application fields can be broadly separated into two categories: classification application and segmentation applications.
- Classification Applications For a given set of labeled images, using the deep learning model to find the patterns between the input images and its corresponding class labels. The related applications, such as lung images detection from CT scanning to classify images patches into 7 classes. This paper describes how to use the CNN model to classify the healthy tissue and six different interstitial lung disease patterns. The other example is to identify the thyroid nodules as malignant or benign from the chest X-ray and Ultrasound images.
- Segmentation Application The other important application for Medical Image Analysis is to identify organs, lesions or substructures of organs from the Ultrasound, MRI or X-Ray images. Now, you can use deep learning models to segment the brain tumors from MRI images. With recent progress in Deep Learning field, this project will build a model and application to detect acute intracranial hemorrhage and its subtypes based on the rich medical image dataset which is provided by the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA®) in collaboration with members of the American Society of Neuroradiology and MD.ai. This is also a Kaggle Featured Prediction Competition launched months ago.
Problem Statement
Intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding that occurs inside the cranium, is a serious health problem requiring rapid and often intensive medical treatment. For example, intracranial hemorrhages account for approximately 10% of strokes in the U.S., where stroke is the fifth-leading cause of death. Identifying the location and type of any hemorrhage present is a critical step in treating the patient.
Diagnosis requires an urgent procedure. When a patient shows acute neurological symptoms such as severe headache or loss of consciousness, highly trained specialists review medical images of the patient’s cranium to look for the presence, location and type of hemorrhage. The process is complicated and often time consuming.
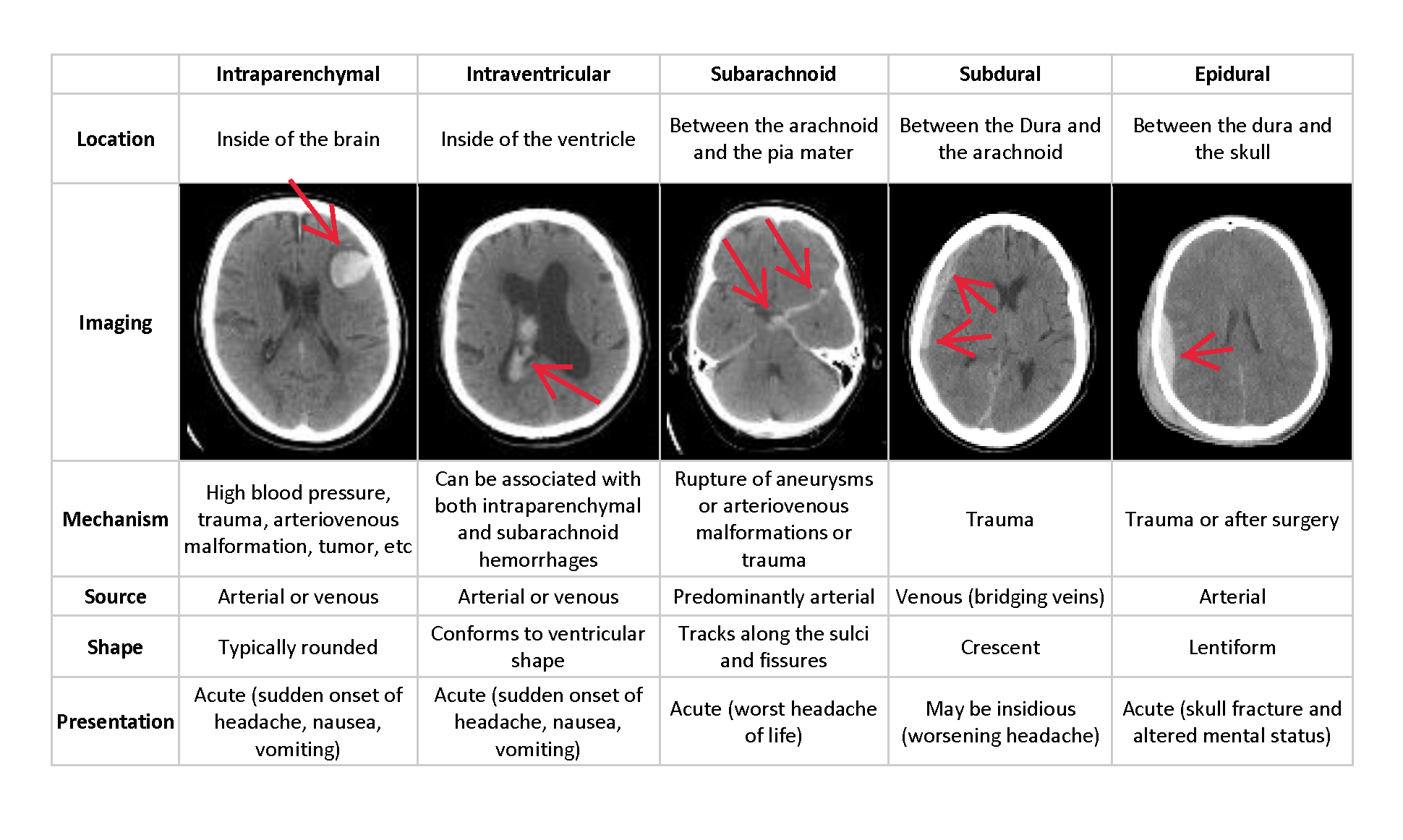
This project is to develop a Classification/Segmentation model and build a web application to identify the five Hemorrhage sub-Types: Intraparenchymal, Intraventricular, Subarachnoid, Subdural and Epidural.
Metrics
This project are are evaluated using a weighted multi-label logarithmic loss. Each hemorrhage sub-type is its own row for every image, and the model will predict a probability for that sub-type of hemorrhage. There is also an ‘any’ label, which indicates that a hemorrhage of ANY kind exists in the image. The ‘any’ label is weighted more highly than specific hemorrhage sub-types. For each image Id, prediction will have a set of predicted probabilities (a separate row for each sub-type). Then taking the log loss for each predicted probability versus its true label. The loss is averaged across all samples. When calculating a weighted multi-label logarithmic loss, predicted input values of 0 and 1 are undefined. To avoid this problem, log loss functions typically adjust the predicted probabilities (p) by a small value (epsilon) and use the MinMax Rule: max(min(p, 1-10-15), 10-15)
Results Summary
Model Evaluation and Validation
ResNet50 Model
Train Data Input: Data Set generator will transform the DICOM image into size 224*224 and channel 3 image as imput Train/Valid/Test Data Split: Use the ShuffleSplit to split the train dataset Model Hyper-parameters: batch size = 32 epochs = 5 Decay_rate = 0.8 Learning rate = 5e-4
Validation Scores: Public Scores: 1% test data: 0.40581 Private Scores : 99% test data: 0.07895
EfficientNet B4 Model
Train Data Input: Data Set generator will transform the DICOM image into size 256*256 and channel 3 image as imput Train/Valid/Test Data Split: Use the MultilabelStratifiedShuffleSplit to split the train dataset Model Hyper-parameters: batch size = 16 epochs = 6 drop_out = 0.2 Learning rate = 1e-4
Validation Scores: Public Scores: 1% test data: 0.73422 Private Scores : 99% test data: 0.17564